Scenario: In the first blog in this series I deployed an Azure AD Directory Services instance which will be used as the directory for my organization. In order to manage the AADDS directory, I need to install ADUC on a VM connected to the AADDS Managed Domain. For this, I need to ensure that my VM’s VNET has network connectivity with the VNET my AADDS is on.
Prior to connecting the VNET when you try to ping the domain or join the VM to the domain, you get an error – due to a lack of network connectivity.
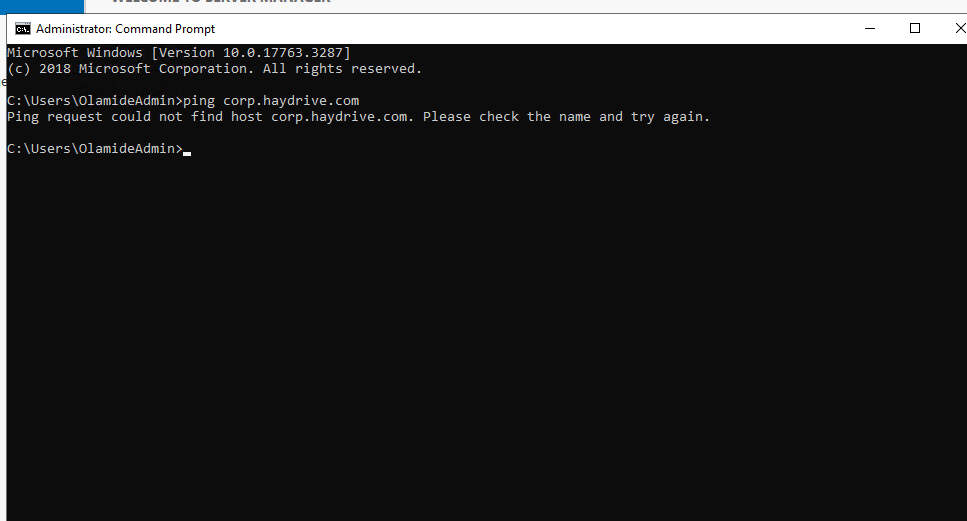
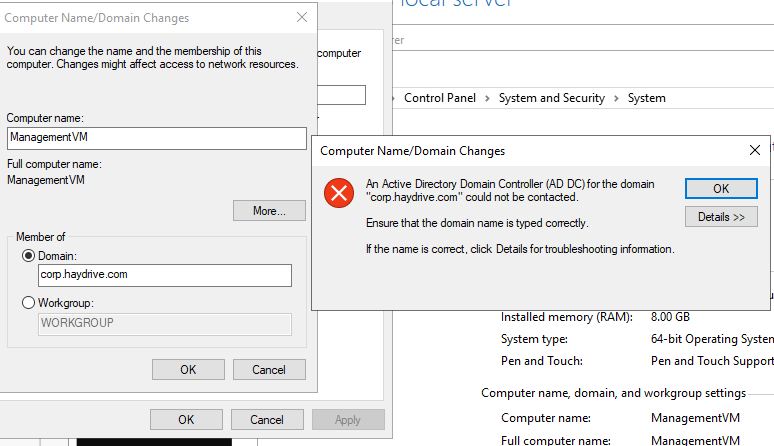
In order to fix the connectivity, I will be peering the VNET associated with my Virtual Machine with the VNET associated with my Azure Active Directory Domain Services environment.
In my setup, I have a VNET for my fictional Edinburgh Office which is where my Management VM is hosted. To peer with the corp AADDS VNET:
- Open the AADDS Vnet, and navigate to the DNS Server section
- Take note of the custom DNS server IP Address which should already be preset with the IP address for the managed domain
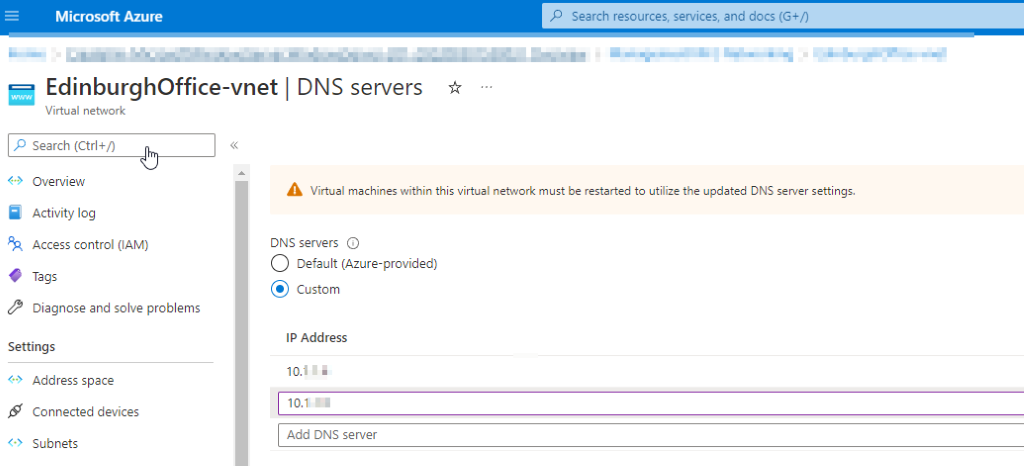
- Open the Second VNET (the VNET we are peering with) and Navigate to the DNS Section
- Change DNS Server to Custom, and Add the Managed Domain IP Address we grabbed earlier
- Hit save
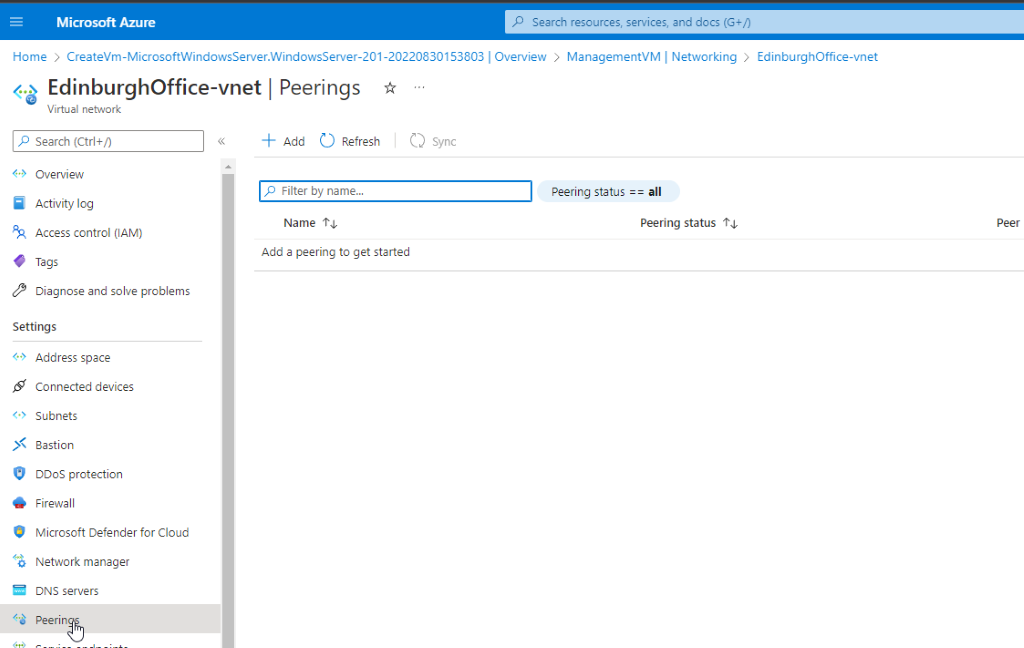
- Click on the peerings tab and click Add peering
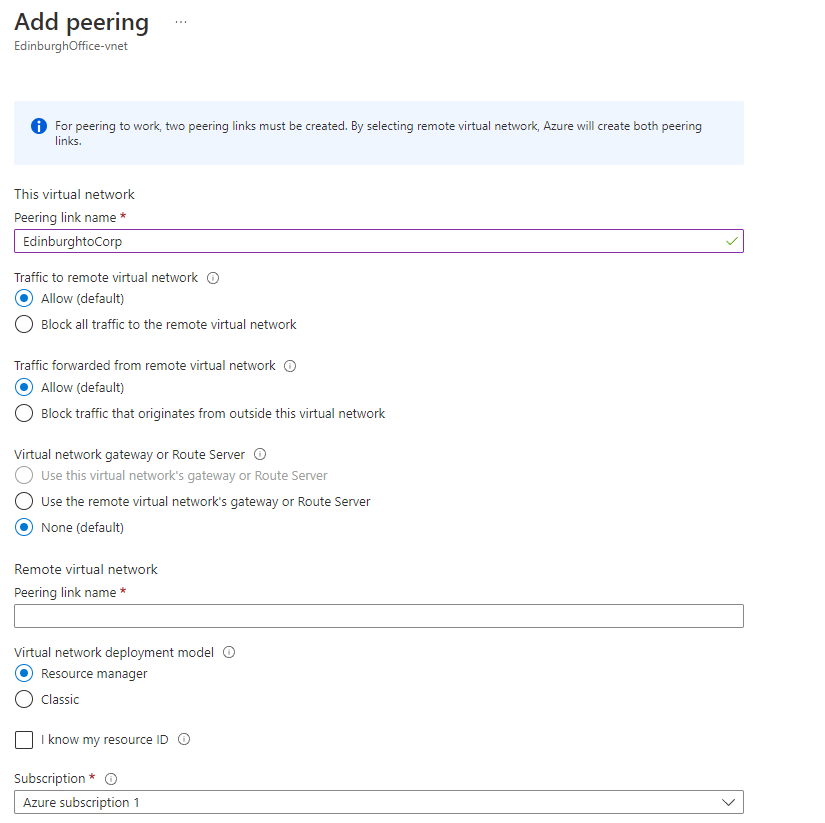
- Give first Peering a memorable name
- Select the Virtual Network to connect to, then click add (this should now peer the two VNETS )
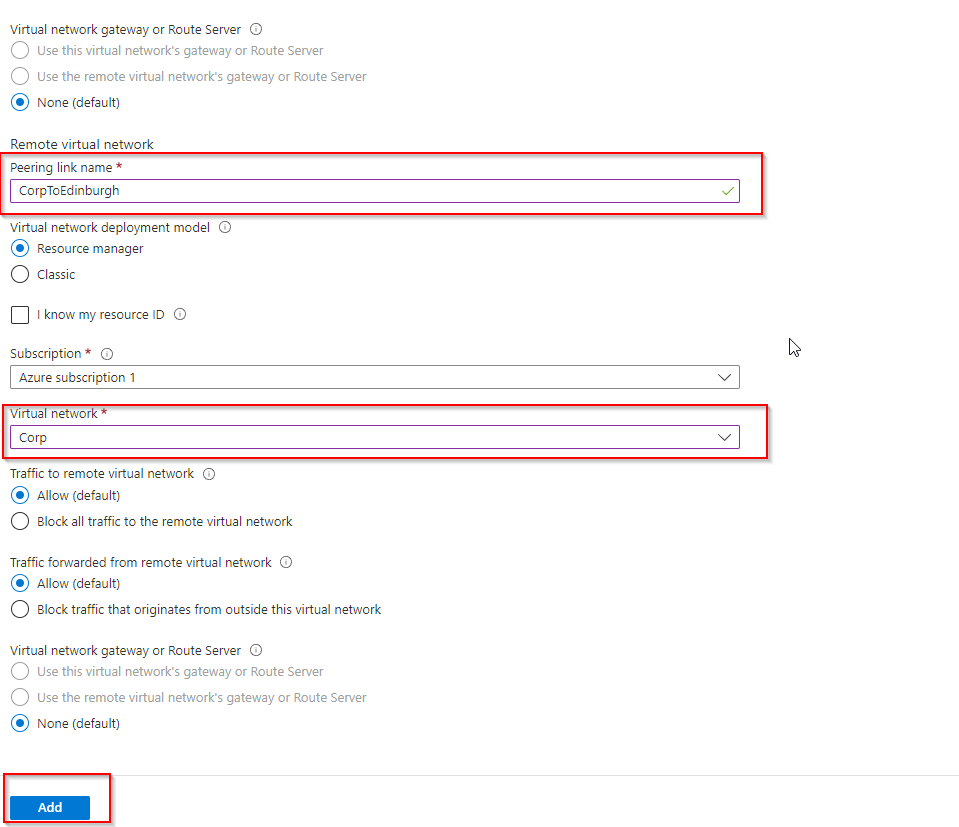
For the VNET peering to reflect on our management server (or any server you are looking to connect) restart the server then try to Ping the Managed Domain again and you should get a response back from the Managed Domain.
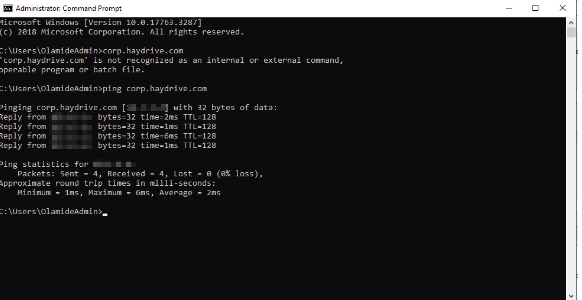
What Have we done?
Connected our AADDS VNET with our Office VNET where the management Server is connected. This enables us to join our management server to the Azure AD Domain Services managed domain.
Sources: